From public health networks to knowledge exchange, Coronavirus 2020 is a thorough evaluation of China’s disaster preparedness and response capability. China has had its main advantage in this epidemic-stopping battle-extensive scientific and technical infrastructure.
As coronavirus disease continued to grow in 2020, more and more groundbreaking techniques are being implemented to tackle the outbreak as well. Technology not only helps to support millions of people’s daily lives in solitary confinement, but it also helps combat the epidemic.
Table of Contents
Gene sequencing technology:
China has completed the sequencing of the viral genome in the first few weeks of the outbreak of coronavirus disease in China. Afterward, China released the gene sequencing findings on related websites, causing a “chain reaction” in research laboratories around the world. Orders for samples synthesized with viruses have risen significantly, and scientists have begun replicating the virus from scratch. It allows new therapies to be tried and even failed tests provide useful hints to guide researchers on where to concentrate.
Drone deployment:
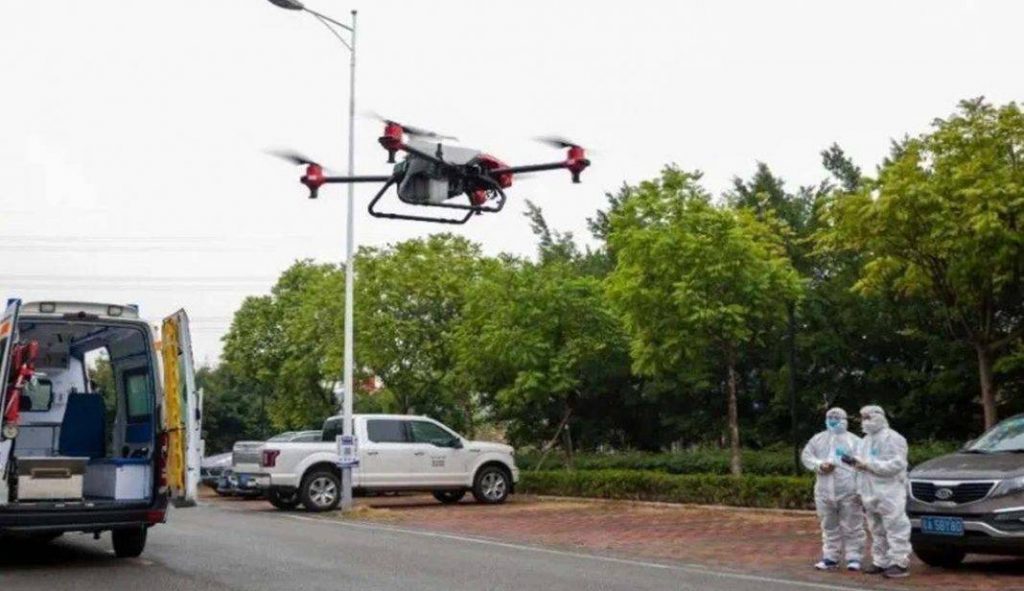

In China, drones are sent to support against the virus. –some drones watch the sidewalk and remind people of “wear a mask on their way” through a high-speaker; others are drones “Keeping” a QR code that goes around the street, which makes it easy for drivers to check their mobile phones for health information to be registered. Applying drones makes it possible for local authorities to release information on disease prevention faster and to maintain a healthy gap in results. Many drones use include the spraying and transport of disinfectants in remote areas.
Smartphones:

Smartphones play a significant part in limiting radiation. The takeaway app offers contactless service, and the delivery person at the designated location will drop the takeaway and health card, which records the temperature of and person involved in cooking and delivering food. There is also an app that provides users with a “confirmed case distribution map” for real-time alerts to mark confirmed cases and their neighborhoods. At the same time, mobile payments reduced the spread of viruses attached to banknotes considerably. Studies have shown banknotes are capable of holding viruses for up to 17 days. China has the highest rate of electronic wallets penetration in the world and two of the largest mobile payment networks, and its sophisticated financial services infrastructure is effectively helping to limit the spread of the epidemic.
Information Epidemics:
As coronavirus diseases were reported extensively around the world in 2020, inaccurate and incorrect knowledge is spreading across the globe. The World Health Organization (WHO) calls such misleading or inaccurate reports “infodemic.” Although technology has encouraged the distribution of false information, it has also helped curb the “information epidemic.” In China, many academics, universities, organizations (including the United Nations Development Programme), celebrities, and even artificial intelligence news anchors are actively coordinating to counter the “information epidemic” and urge everyone to start from their side and contribute to propaganda prevention. For example, sharing how to wear a mask, sharing accurate official information on disease prevention provided by WHO with the elderly and other vulnerable people, and promoting a social distance of 1 meter.
Online Office:

A big problem during the prevention and control of epidemics is that usually, many people cannot rework. Many technology firms provide free online communication resources at this time. Additionally, several businesses have rapidly embraced the home office approach, using electronic meeting tools, networking networks, and LBS systems for check-in, and simply ensuring workers stay home and work. Participants use the Zoom conference call and forum for business resource planning to sustain their regular work in the United Nations Development Programme.
Online Education:

The greatest problem for parents after weeks of school suspension could be how to get their kids to finish school. A number of Chinese schools have launched online learning platforms to achieve this. On the web, students listen to online lectures, and teachers teach at home via the live broadcast app.
Students use online research sites at home.
E-medicine and psychotherapy:
There are several other medical needs, in fact, ranging from hypertension to arthritis. During the prevention and control of the epidemic, people were concerned that going to the hospital to see a doctor might cause cross-infection, so the demand for online consultation and drug delivery rose sharply. Some organizations now provide free online advice to help people deal with “social isolation” tension.
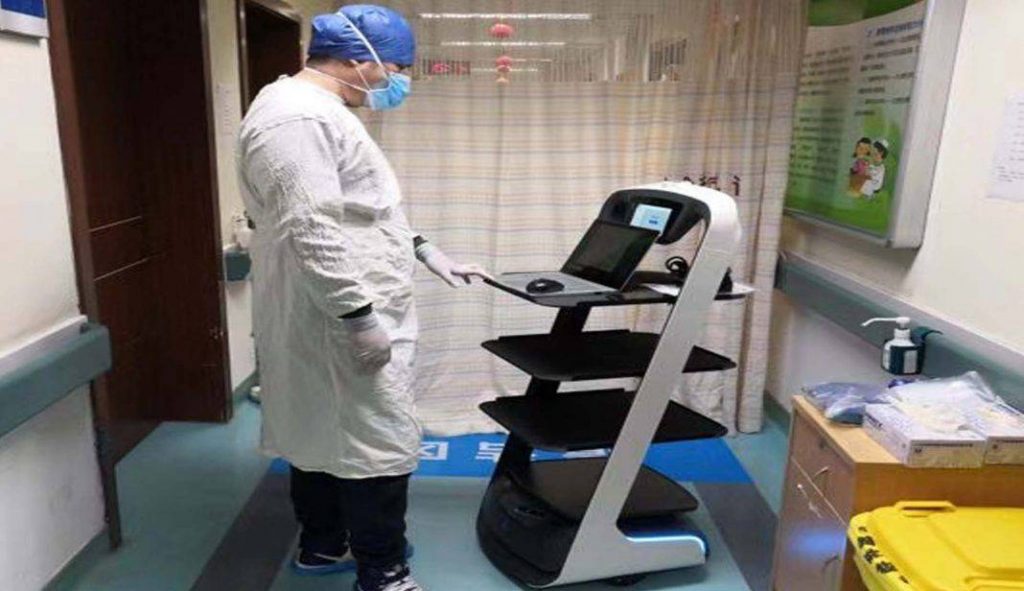
Robotic nurses and artificial intelligence diagnosis:
Several hospitals in China have also started using robots to supply patients with food, medications, and other materials, disinfect hospitals and other public spaces, monitor patient temperature, and answer common questions. Artificial intelligence can read thousands of CT scans in 20 seconds in the process of diagnosing coronavirus 2019, with an accuracy rate of about 96 percent.
Online social:
Forced steps of separation influence the everyday life and social interactions of about a quarter of the world’s population. So millions of people choose to connect through the Internet. The family had dinner with friends and relatives who were far away and toasting with drinks in front of the camera. In the VR, even some weddings were held during the epidemic.
Big data dashboards:

Transparent, open public information has encouraged the creation of information dashboards to monitor the epidemic’s spread. During this battle against disease prevention, not only UN agencies such as WHO have created and generated big data dashboards, but a number of contributions have also been made by smaller organizations and businesses. Users can access this updated information and data in real-time easily through widely used and familiar apps.
Since the use of technology often poses its particular problems and raises questions about privacy and the public interest. But science and technology have also provided medical, intelligence, assistance, food, education, and security assistance too many people in the fight against the 2020 coronavirus epidemic, and its role is crucial.
So that’s Ten ways science can help fight Coronavirus 2020 in China Gettopten got, I would like to invite you to share your experience in the comment section. If you have more suggestions please contact us.










